Hydrogen is a clean type of fuel that generates just water when used in a fuel cell. Natural gas, nuclear power, biomass, and renewable energy sources such as the sun and wind may all be used to make hydrogen. These characteristics make it an appealing fuel choice for transportation and power production applications. It may be utilized in automobiles, housing, portable power, and a variety of other applications.
Hydrogen is a type of energy carrier that may be utilized to store, transport, and transfer energy from other sources. Today hydrogen fuel may be manufactured in a variety of ways. Natural gas reformation (a thermal process) and electrolysis are the most often used technologies nowadays. Other approaches include solar-powered and biological processes. Hydrogen may be created using a variety of home resources, such as fossil fuels, biomass, and water electrolysis with electricity. The environmental effect and energy efficiency of hydrogen are determined by its production method. Several efforts are now ongoing to reduce the costs of hydrogen generation.
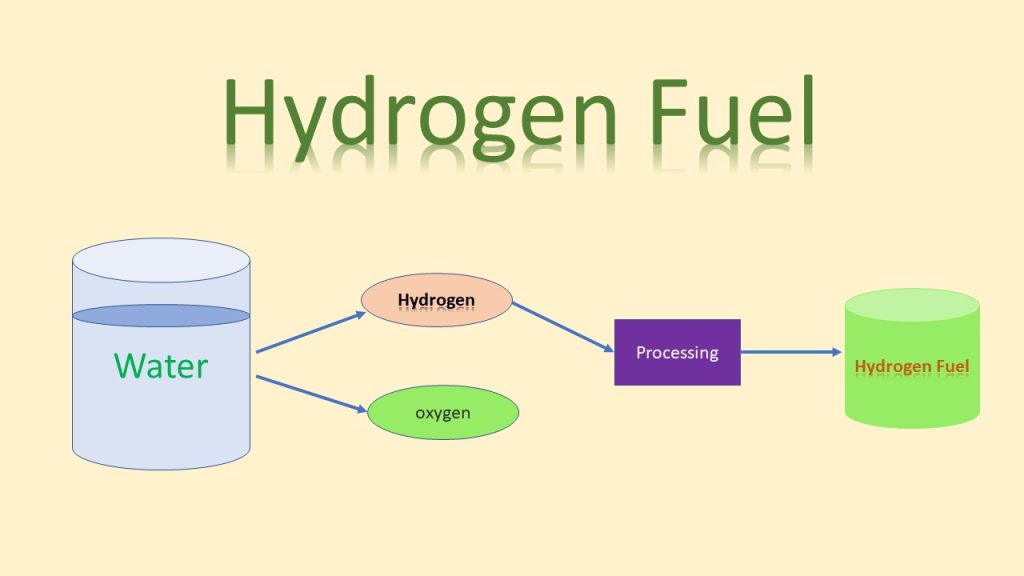
Hydrogen fuel cells generate energy by mixing oxygen and hydrogen atoms. To generate water, electricity and tiny amounts of heat, hydrogen combines with oxygen in an electrochemical cell similar to that of a battery. There are several types of fuel cells available for a wide variety of uses. Around room temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a gas; however, at -423 degrees Fahrenheit, hydrogen condenses to a liquid (minus 253 degrees Celsius). Hydrogen fuel is hydrogen that is used as a fuel with oxygen. It is zero-carbon if it is produced in a non-carbon-based technique. It is suitable for use in fuel cells and internal combustion engines.
Hydrogen is the lightest and most plentiful element in the universe, so on paper, hydrogen fuel has a lot going for it. Although it seldom occurs on its own on Earth, it can be created by splitting nearly endless water molecules with clean energy, leaving just oxygen as a byproduct. However, currently, 96 percent of hydrogen is produced directly from fossil fuels, mostly natural gas, followed by coal, and then oil. This is mostly accomplished by a process known as steam reformation, which emits carbon dioxide.
Every year, approximately 70 million tons of hydrogen are produced, primarily for the production of ammonia fertilizer and chemicals such as methanol, as well as to remove impurities during oil refining. Proponents of hydrogen as a clean fuel believe it will be available soon.
To know about Advantages of nanotechnology click_here>>






Pingback: Details About Electrical cars | how electric car works
This is really very good articles. I get a lot’s of new and important information here. Thanks you so much.